Build your own Data Commons
- Overview
- Why use a custom Data Commons instance?
- Comparison between base and custom Data Commons
- System overview
- Requirements and cost
- Recommended workflow
Overview
A custom instance natively joins your data and the base Data Commons data (from datacommons.org) in a unified fashion. Your users can visualize and analyze the data seamlessly without the need for further data preparation.
You have full control over your own data and computing resources, with the ability to limit access to specific individuals or open it to the general public.
Note that each new Data Commons is deployed using the Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Why use a custom Data Commons instance?
If you have the resources to develop and maintain a custom Data Commons instance, this is a good option for the following use cases:
- You want to host your data on your own website, and take advantage of Data Commons natural-language query interface, and exploration and visualization tools.
- You want to add your own data to Data Commons but want to maintain ownership of the Cloud data.
- You want to add your own data to Data Commons but want to customize the UI of the site.
- You want to add your own private data to Data Commons, and restrict access to it.
For the following use cases, a custom Data Commons instance is not necessary:
- You want to share your data publicly on datacommons.org. In this case, please file a data request in our issue tracker to get started.
- You want to make the base public data or visualizations available in your own site. For this purpose, you can call the Data Commons APIs from your site; see Data Commons web components for more details.
Comparison between base and custom Data Commons
| Feature | Base Data Commons | Custom Data Commons |
|---|---|---|
| Interactive tools (Exploration tools, Statistical Variable Explorer, etc.) | yes | yes |
| Natural language query interface | yes, using Google AI technologies and models | yes, using open-source models only1 |
| Model Context Protocol (MCP) server | yes | yes |
| REST APIs | yes | yes |
| Python and Pandas API wrappers | yes | yes |
| Google Spreadsheets | yes | no2 |
| Site access controls | n/a | yes, using any supported Cloud Run mechanisms3 |
| Fine-grained data access controls4 | no | n/a |
- Open-source Python ML library, Sentence Transformers model, from https://huggingface.co/sentence-transformers.
- If you would like to support this facility, please file a feature request.
- For example, Virtual Private Cloud, Cloud IAM, and so on. Please see the GCP Restricting ingress for Cloud Run for more information on these options.
- You cannot set access controls on specific data, only the entire custom site.
System overview
Essentially, a custom Data Commons instance is a mirror of the public Data Commons, that runs in Docker containers hosted in the cloud. In the browsing tools, the custom data appears alongside the base data in the list of variables. When a query is sent to the custom website, a Data Commons server fetches both the custom and base data to provide multiple visualizations. At a high level, here is a conceptual view of a custom Data Commons instance:
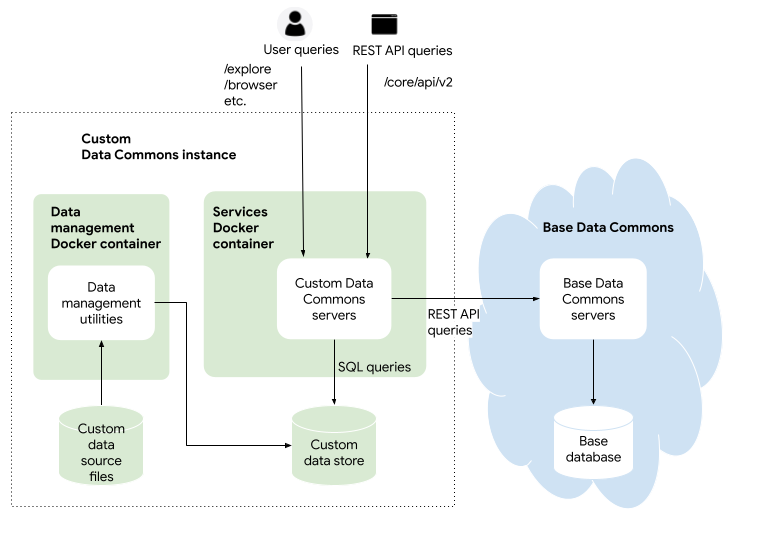
A custom Data Commons instance uses custom data that you provide as raw CSV files. An importer script converts the CSV data into the Data Commons format and stores this in a SQL database. For local development, we provide a lightweight, open-source SQLite database; for production, we recommend that you use Google Cloud SQL.
Note: You have full control and ownership of your data, which will live in SQL data stores that you own and manage. Your data is never transferred to the base Data Commons data stores managed by Google; see full details in this FAQ.
In addition to the data, a custom Data Commons instance consists of two Docker containers:
- A “data management” container, with utilities for managing and loading custom data and embeddings used for natural-language processing
- A “services” container, with the core services that serve the data and website
Details about the components that make up the containers are provided in the Quickstart guide.
Requirements and cost
A custom Data Commons site runs in Docker containers on Google Cloud Platform (GCP), using Google Cloud Run, a serverless solution that provides auto-scaling and other benefits. You will need the following:
- A GCP billing account and project
- A Docker account
- If you will be customizing the site’s UI, familiarity with the Python Flask web framework and Jinja HTML templating
Note: Data Commons does not support local Windows development natively. If you wish to develop Data Commons on local Windows, you will need to use the Windows Subsystem for Linux. Otherwise, you can use the free Google Cloud Shell as a (remote) development environment.
In terms of development time and effort, to launch a site with custom data in compatible format and no UI customization, you can expect it to take less than three weeks. If you need substantial UI customization it may take up to four months.
The cost of running a site on Google Cloud Platform depends on the size of your data, the traffic you expect to receive, and the amount of geographical replication you want. For a singly-homed service with 5 GB of data serving 1 M queries per month, you can expect a cost of approximately $400 per month.
You can get precise information and cost estimation tools at Google Cloud pricing. A GCP setup must include:
- Cloud SQL
- Cloud Storage
- Cloud Run: Job + Service
- Artifact Registry (< 1 GB storage)
You may also need Cloud DNS, Networking - Cloud Loadbalancing, and Redis Memorystore + VPC networking (see Launch your Data Commons for details).
Recommended workflow
- Work through the Quickstart page to learn how to run a local Data Commons instance and load some sample data.
- Prepare your real-world data and load it in the local custom instance. Data Commons requires your data to be in a specific format. See Prepare and load your own data for details.
Note: This section is very important! If your data is not in the scheme Data Commons expects, it won’t load.
- If you want to customize the look of the feel of the site, see Customize the site and Build a custom image.
- Optionally, configure an AI agent to send NL queries to the MCP server (via an LLM). See Run MCP tools.
- When you have finished testing locally, set up a development environment in Google Cloud Platform. See Deploy to Google Cloud.
- Productionize and launch your site for external traffic. See Launch your Data Commons.
- For future updates and launches, continue to make UI and data changes locally, before deploying the changes to GCP.
Page last updated: February 26, 2026 • Send feedback about this page